What is CBD?
- Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive chemical in cannabis
- It is associated with many of the plant’s medicinal properties
- It is legal to buy and sell in the UK as a “food supplement”
- This article will help explain how CBD works in the human body
Many would argue that cannabis owes the majority of its medicinal and therapeutic properties to cannabidiol (CBD), one of the 100+ known cannabinoids (chemicals) found on the cannabis plant.
These cannabinoids are specifically found on the glandular hairs of the plant, called trichomes, along with hundreds of terpenoids (terpenes) which gives different cannabis strains their distinct tastes and scents. They, along with cannabinoids, create cannabis’ therapeutic effects.
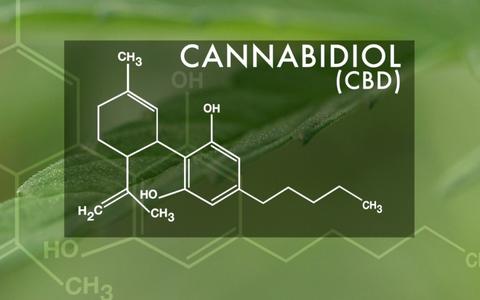
Over the past few years, CBD has been showing great potential in alleviating symptoms of medical ailments, such as epilepsy, MS, mental illnesses (such as anxiety and depression, ADHD and even chronic pain.
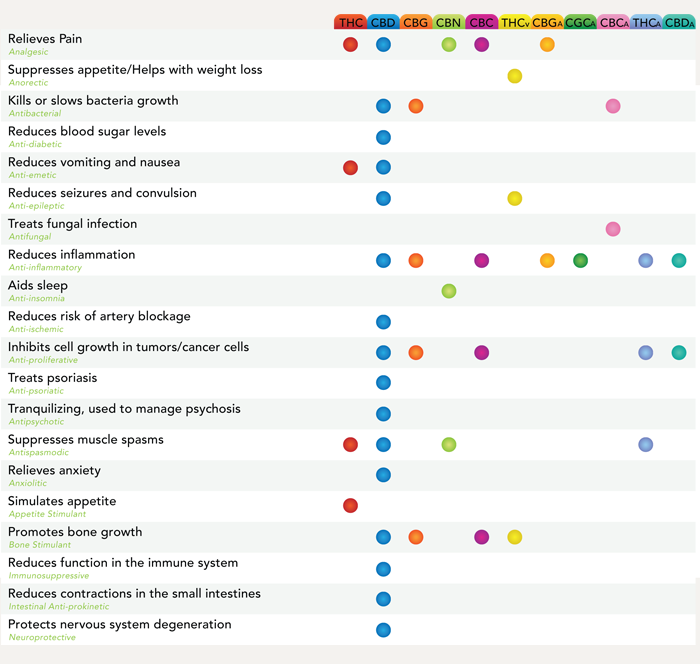
This is because CBD acts as an anti-convulsive; anti-cancer, sedative, hypnotic, anti-psychotic, anti-nausea and even as an anti-inflammatory. Cannabidiol is a pleiotropic drug so it produces its many effects through multiple molecular pathways.
Despite cannabis’ effects coming mostly from its cannabinoids and their interactions with our endo-cannabinoid system (CB1 and CB2 receptors), CBD actually has little affinity for either of the receptors.
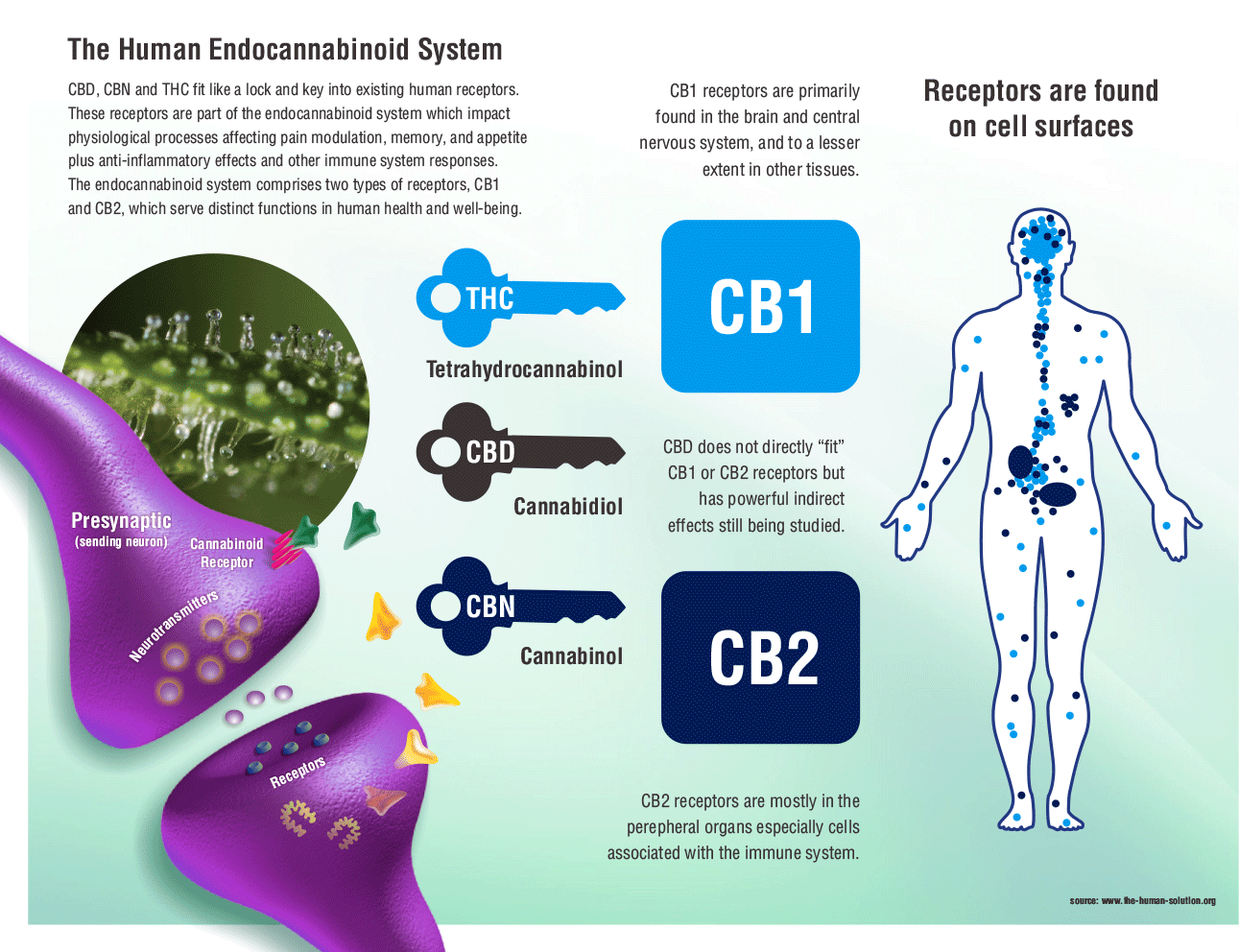
In fact, CBD activates several non-cannabinoid receptors and ion channels. Jose Alexandre Crippa and his colleagues at the University of San Paulo in Brazil and King’s College in London conducted pioneering research into CBD and the neural correlates of anxiety.
In high concentrations, CBD activates the 5-HT1A (hydroxytryptamine) serotonin receptor, giving cannabis its anti-anxiety effect.
Serotonin has many roles in the body, including (but not limited to) anxiety, addiction, appetite, sleep, pain perception, nausea and vomiting.
All these areas can be affected by consuming CBD.
A key point to make here is that CBD itself is not actually naturally present in cannabis, and the same goes for THC. Their precursors, THCA and CBDA (A = acid) are naturally present and are converted using heat during cooking or smoking, into their more commonly known counterparts.
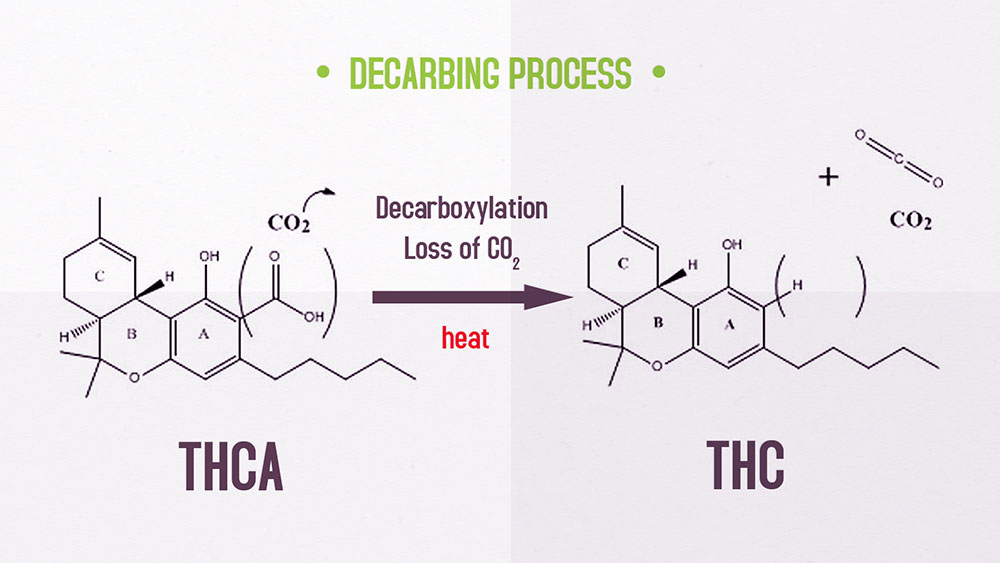
The precursors, however, have shown to be very healthy to consume; THCA providing anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective properties and more.CBDA also has a strong affinity for the 5-HT1A receptor (even more so than CBD).
Preclinical studies indicate CBDA is a potent anti-emetic, stronger than either CBD or THC, which also have anti-nausea properties.
“Hopefully, access for [CBD] products will help patients… who cannot obtain medication that contains THC”
– Dr. Perry Solomon
]With all this information emerging from CBD and its interactions, it is easy to forget about the hundreds of other chemicals present in cannabis and their effects.
CBD isolates can be very useful for patients with specific conditions or for those who do not wish to feel the psychoactive effects of THC.
Many studies, however, have suggested that cannabis’ compounds are far more effective when used in conjunction with each other, in what is known as the “entourage effect.”
In other words, the medicinal impact of the whole plant, is greater than the sum of its constituents.
A 1:1 ratio of CBD to THC is generally considered to be the most effective for medicinal benefits, including cancer therapy.
This interactive synergy between cannabis compounds has been termed the “entourage effect,” and shows why isolated THC and/or CBD therapies may not be the most efficient in treating various medical conditions.
In the years following the media frenzy of Charlotte’s Web, a non-psychoactive cannabis strain that was processed into a CBD-rich oil for an epileptic child, CBD therapies have been very much on the rise.
Several countries and state laws have now regulated to allow CBD isolated medicines.
But while CBD-only medicines have been life-changing for many individuals, these laws are there mainly to help those suffering from epileptic seizures. There is currently a great deal of confusion surrounding the difference between oils made from CBD or from “hemp.”
Hemp and cannabis both come from the same species of plant; Cannabis Sativa.
The main obvious differences is that hemp contains “trace levels” of THC (practically 0%), whereas cannabis contains much higher levels.
Hemp, however, does contain CBD and other cannabinoids and terpenes. Meaning ingesting hemp flower in any way will not have psychoactive effects, but it can still have a relaxing effect due to its CBD and other cannabinoid content.
Hemp oil, more commonly known as hemp seed oil, is produced by pressing hemp seeds to extract the fatty oils within.
These oils are incredibly nutritious and carry a number of uses from cooking to cosmetic products.
However, due to their extraction method from seeds, the oil does not contain high enough CBD levels to be considered for use medicinally.
CBD oil can be extracted using a number of processes such as butane or propane extraction, or the cleanest but most expensive method: CO2 extraction, which uses no toxic substances.
Hemp flowers can be used to extract CBD oil, however medicinal strains of cannabis are used for the high quality CBD oil used medicinally.
These strains are bred to be high in CBD and generally have little or almost no THC content. Hemp oil is, generally, not considered for medicinal use, even though it is highly nutritious.
A huge 25% of its calories come from protein, and 30% from its oils, and it is a great source of Omega-3, Omega-6, Phosphorus, Vitamin E, Potassium, Magnesium, Vitamin B1 and Vitamin B2.
So despite it being hard for science to define it as a medicine, many patients still view hemp oil as just that.
Whether you need a CBD isolate, or you wish to make the most of the plant in its full glory and go for a whole plant medicine, Cannabidiol is sure to feature in many health routines in the near future.
Words by Fergus Simpson
References and further Reading
Largest survey on CBD finds nearly half of users are able to stop taking traditional medications
